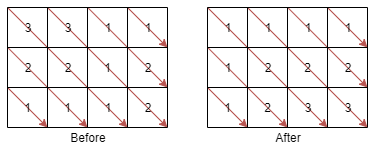
30. Sort the Matrix Diagonally
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]]
Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]Input: mat = [[11,25,66,1,69,7],[23,55,17,45,15,52],[75,31,36,44,58,8],[22,27,33,25,68,4],[84,28,14,11,5,50]]
Output: [[5,17,4,1,52,7],[11,11,25,45,8,69],[14,23,25,44,58,15],[22,27,31,36,50,66],[84,28,75,33,55,68]]Solution:
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> diagonalSort(vector<vector<int>> &mat)
{
int n = mat.size();
int m = mat[0].size();
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
mp[i - j].push_back(mat[i][j]);
}
}
for (auto itr = mp.begin(); itr != mp.end(); itr++)
{
sort(itr->second.begin(), itr->second.end());
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
int idx = i - j;
mat[i][j] = mp[idx].back();
mp[idx].pop_back();
}
}
return mat;
}
};Last updated