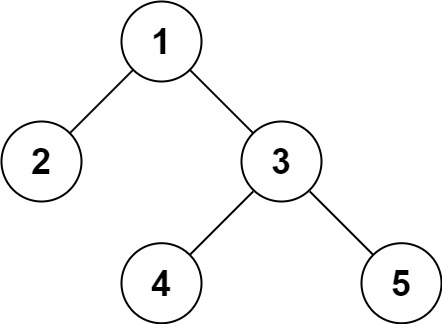
29. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]Input: root = []
Output: []Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]Input: root = [1,2]
Output: [1,2]Solution:
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Codec
{
public:
TreeNode *createTree(queue<string> &q)
{
if (q.empty())
{
return NULL;
}
string k = q.front();
q.pop();
if (k == "#")
{
return NULL;
}
int num = stoi(k);
TreeNode *t = new TreeNode(num);
t->left = createTree(q);
t->right = createTree(q);
return t;
}
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return "#";
}
string lt = serialize(root->left);
string rt = serialize(root->right);
return to_string(root->val) + ',' + lt + ',' + rt;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode *deserialize(string data)
{
queue<string> q;
int start = 0;
int token = ',';
int end = data.find(token);
while (end != -1)
{
string k = data.substr(start, end - start);
q.push(k);
start = end + 1;
end = data.find(token, start);
}
string k = data.substr(start, end - start);
q.push(k);
TreeNode *t = createTree(q);
return t;
}
};Last updated