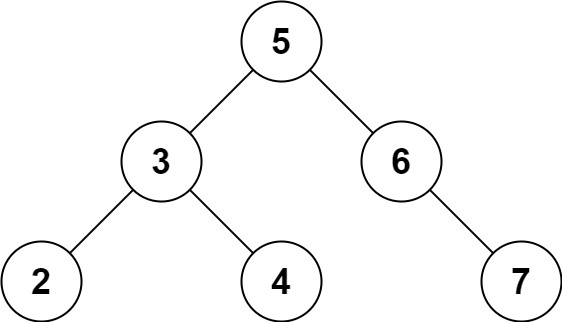
11.Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9
Output: trueInput: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 28
Output: falseSolution: (BFS + SET)
class Solution
{
public:
bool findTarget(TreeNode *root, int k)
{
unordered_set<int> s;
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *t = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = t->val;
if (s.find(k - x) != s.end())
{
return true;
}
s.insert(x);
if (t->left)
{
q.push(t->left);
}
if (t->right)
{
q.push(t->right);
}
}
return false;
}
};Solution: (Using BST)
Last updated