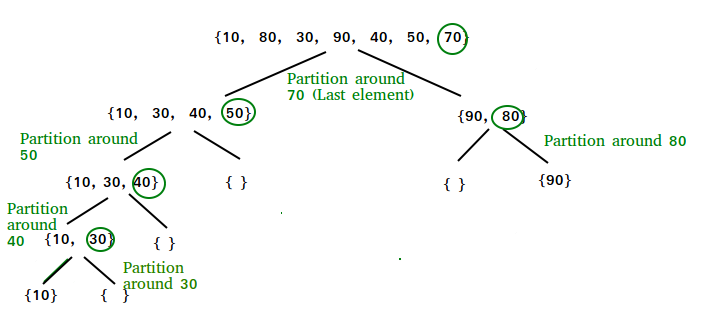
Quick Sort
/* low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */
quickSort(arr[], low, high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now
at right place */
pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); // Before pi
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); // After pi
}
}/* This function takes last element as pivot, places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
partition (arr[], low, high)
{
// pivot (Element to be placed at right position)
pivot = arr[high];
i = (low - 1) // Index of smaller element
for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap arr[i] and arr[j]
}
}
swap arr[i + 1] and arr[high])
return (i + 1)
}
Code
Last updated