31. Minimum Falling Path Sum
Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]]
Output: 13
Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum underlined below:
[[2,1,3], [[2,1,3],
[6,5,4], [6,5,4],
[7,8,9]] [7,8,9]]Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]]
Output: -59
Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is underlined below:
[[-19,57],
[-40,-5]]Input: matrix = [[-48]]
Output: -48Solution: (DP)
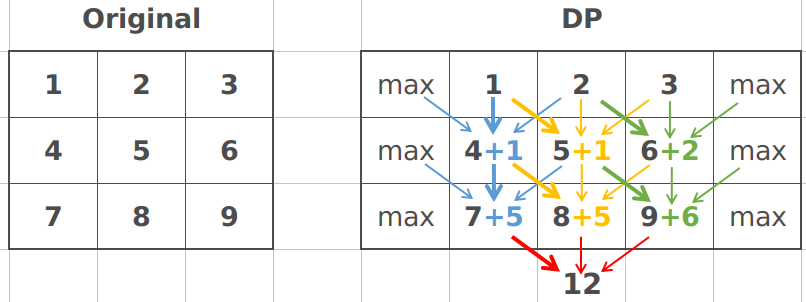
Solution: (Optimized DP)
Last updated