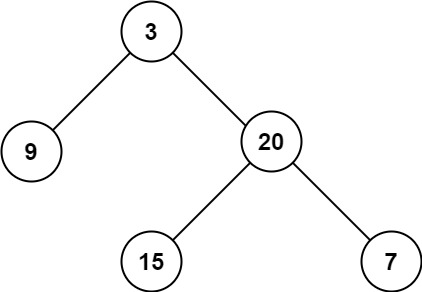
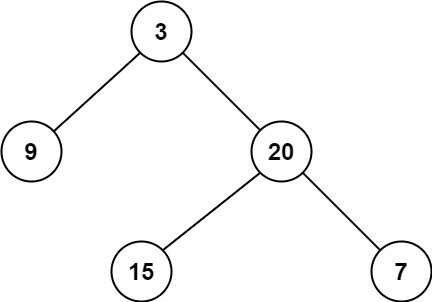
1.Maximum/Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2Input: root = []
Output: 0Input: root = [0]
Output: 1Solution I : (Using level order traversal)
class Solution
{
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL){return 0;}
TreeNode *t = root;
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(root);
int s = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
int k = q.size();
while (k > 0)
{
TreeNode *p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (p->left != NULL)
{
q.push(p->left);
}
if (p->right != NULL)
{
q.push(p->right);
}
k--;
}
s++;
}
return s;
}
};Solution II: Recursive
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Solution
Last updated