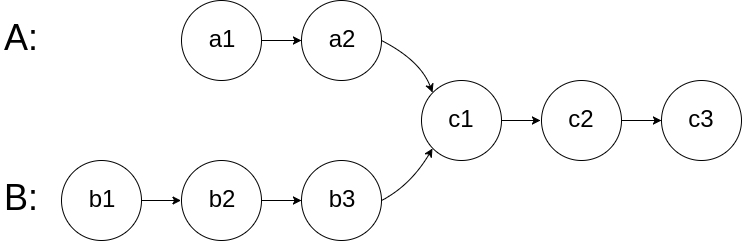
6.Point of insertion between two Linked List
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Intersected at '8'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Intersected at '2'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: No intersection
Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.Solution:
Last updated