13.Reverse a Linked List
Various implementation to reverse a linked list
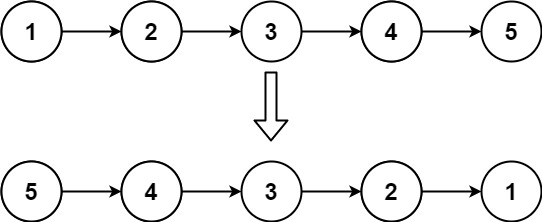
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
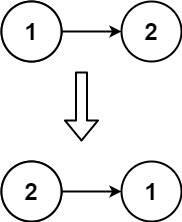
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]Input: head = []
Output: []struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};Method 1:-
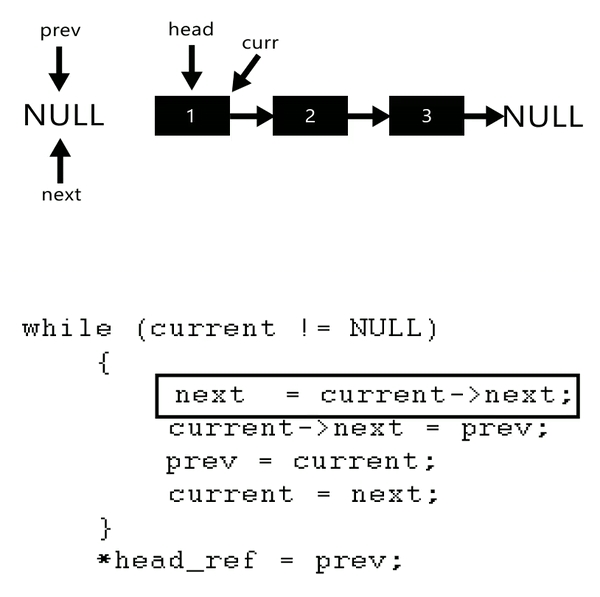
Method 2:- (using Prev, cur and next pointer)
Last updated